What Is Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a language-based disorder that interferes with learning to read. This difficulty happens at both the foundational level of learning and at the word level of learning.
Learning to read and write are two abilities tied to our underlying oral language skills. When we learn to read and write, we repurpose many of the foundational skills we use to listen and speak.
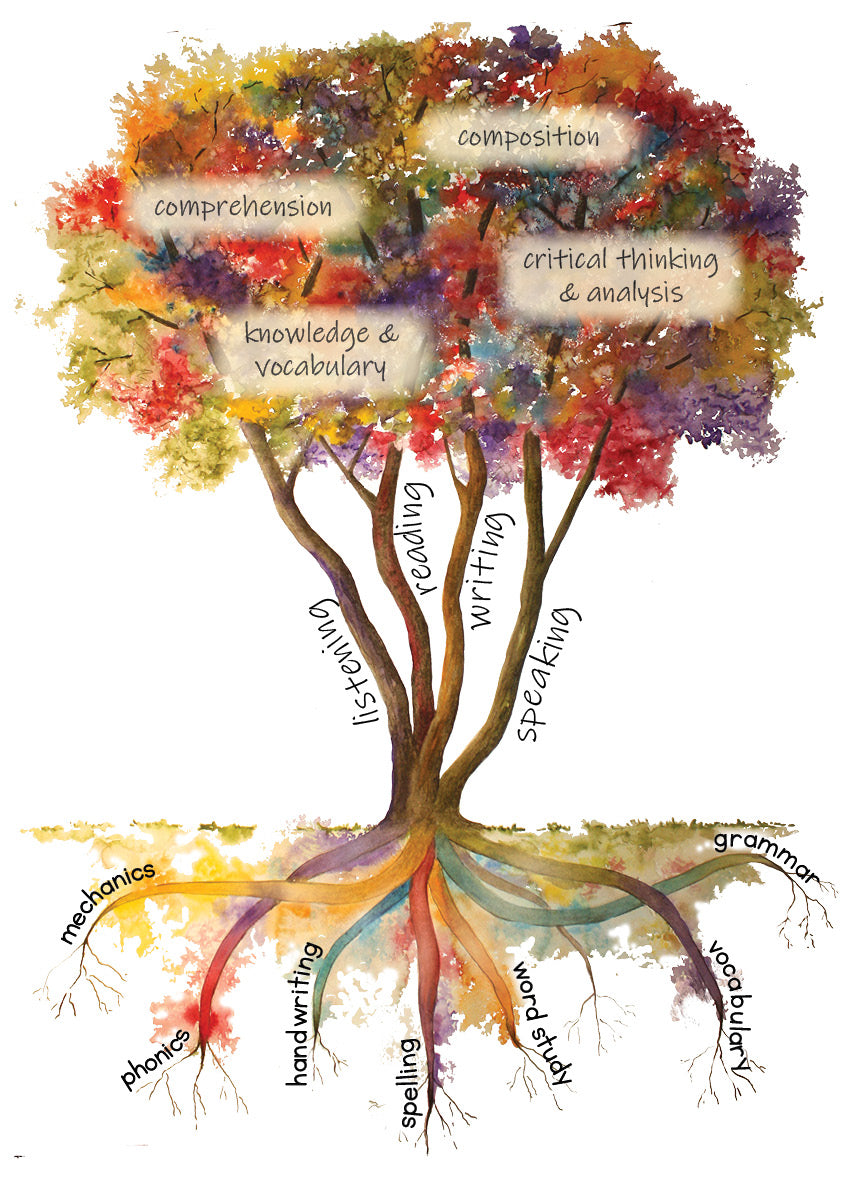
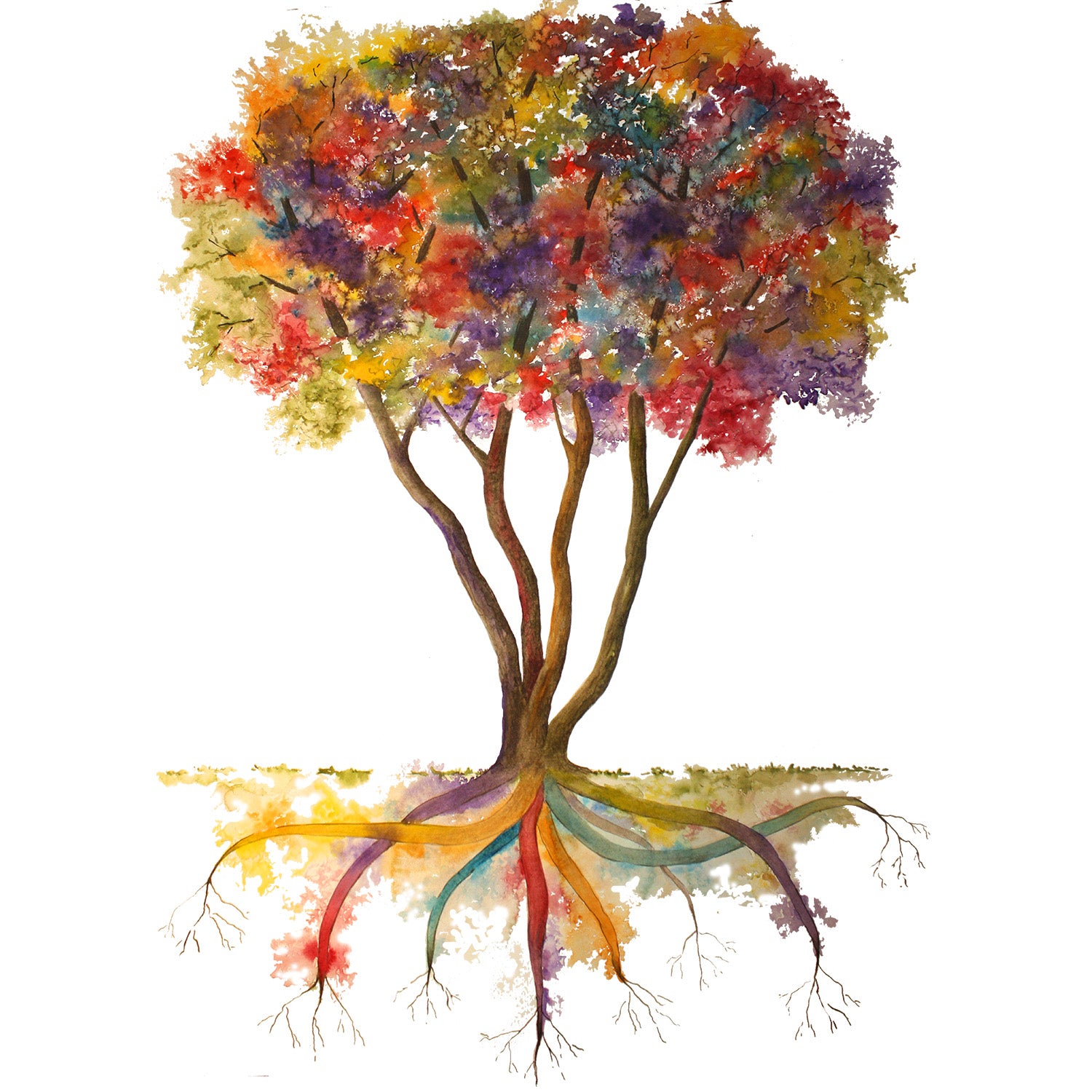
Our language tree shows the relationship of the 4 modes of language:
listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
The roots represent some of the underlying skills needed to learn. The canopy shows an overview of the resulting abilities that are developed over time.
Skills that connect written words to meaning and usage are called lexical skills. These are represented by our tree’s trunks, and some of the roots of vocabulary and grammar.
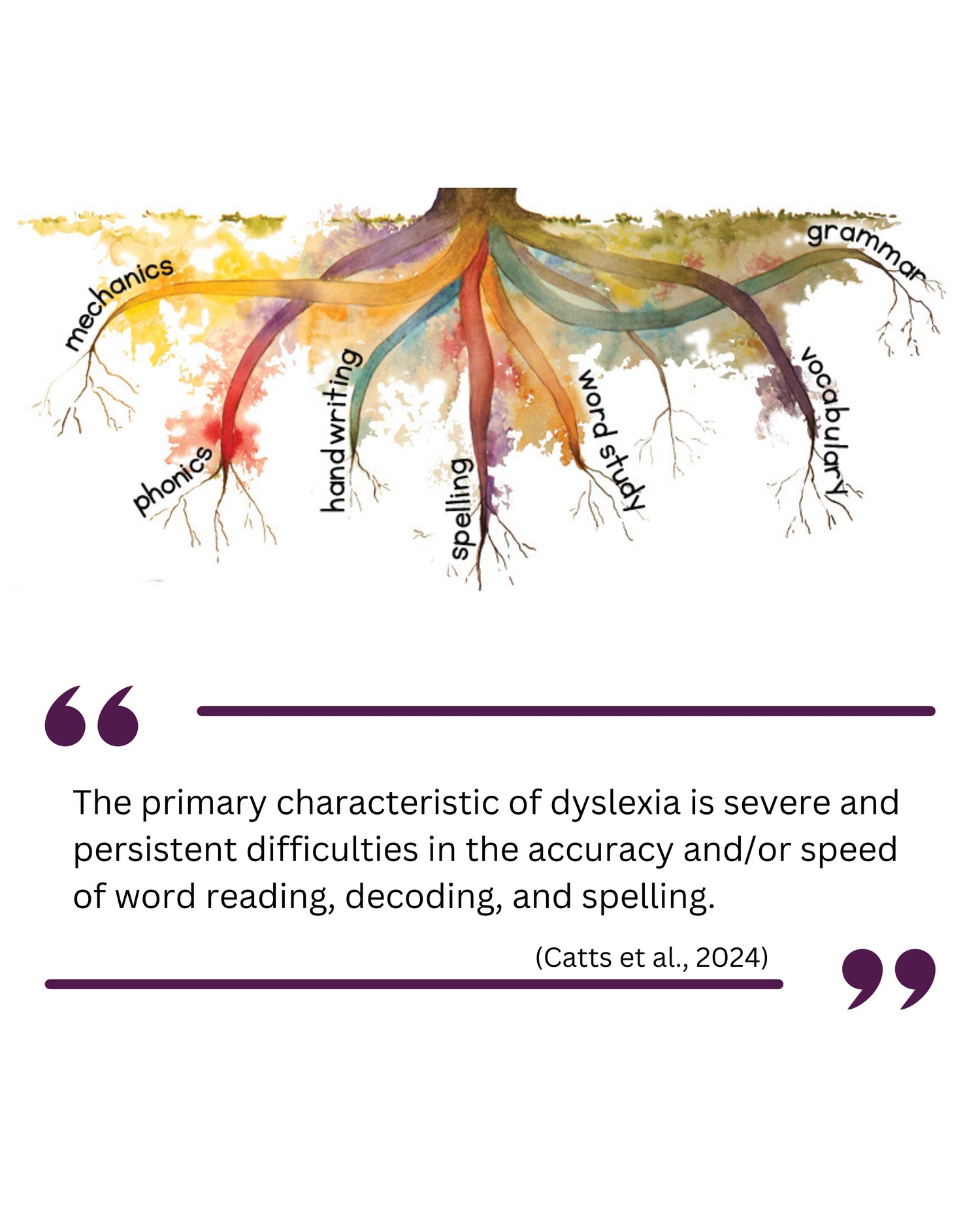
Foundational skills include word-level skills that need to become automatic in order to read fluently and spell accurately. Think of these as the roots of literacy.
Dyslexia is a weakness at an even deeper level, known as sublexical skills. Children with dyslexia find it difficult to learn and recall the sound-to-letter connections needed to easily and quickly read words.
These sublexical skills include:
- phonological processing
- phonological memory
- learning letter names easily and rapidly
- learning letter sounds easily and rapidly
- developing automatic sound-to-letter connections
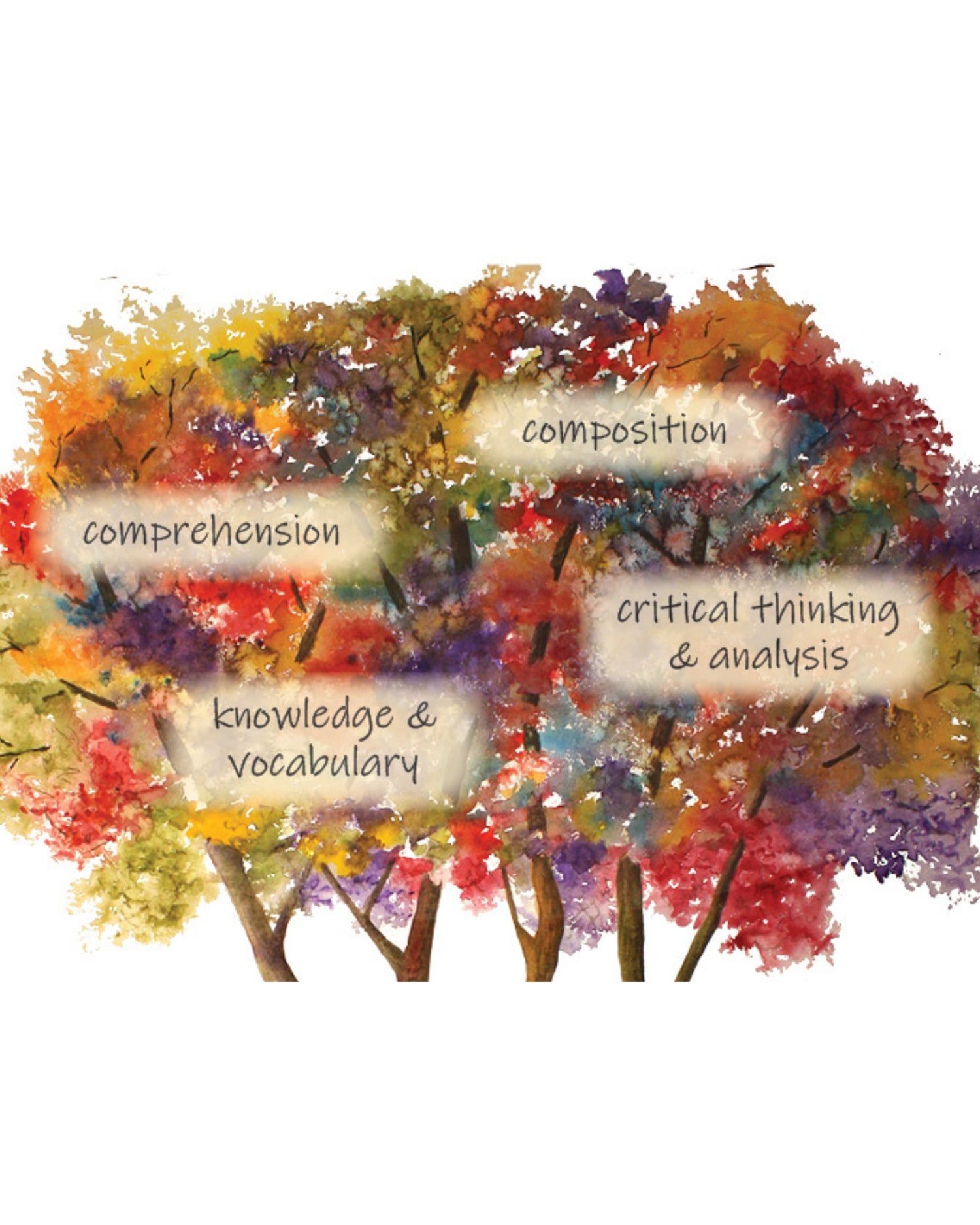
Because students with dyslexia have a combination of sublexical and lexical weaknesses, impeding automatic word memory for fluent reading and accurate spelling, they experience a significant cognitive burden when trying to read and write.
Without efficient reading skills, students struggle to access the higher-level thinking skills needed for advanced literacy tasks, as shown in the tree’s canopy. As a result, students with dyslexia often demonstrate cognitive overload, including increased fatigue, poor attention, weak reading comprehension, reduced writing output, and writing below grade level.
Download a summary of this information:
How Do I Know If My Student Has Dyslexia?
The three most common causes of reading and writing struggle are Dyslexia, Dysgraphia, and Developmental Language Disorder. Each of these disorders has typical indicators. However, some symptoms can overlap. Download our checklist below to help you better understand your student and determine if they show signs of dyslexia.
Download a Checklist of Indicators
We discuss more about the most common causes of reading and writing struggle in this video.
How Can I Help My Student with Dyslexia?
Kids with dyslexia need caring adults who take the time to support them and find the teaching methods and resources they need. Kudos to you for gaining knowledge and pursuing answers to help your learner!

Teaching children with dyslexia demands specific instruction that includes the following:
- Research-based teaching strategies
- Explicit and systematic instruction to establish strong sound-to-letter connections
- Teaching reading and writing together with spelling
- Working from the student’s oral language system to their growing literacy system
- Establishing the phonological strategy of the student saying sounds as they write words
- Consistent and targeted practice routines at least five days per week
- Periodic review to help solidify new learning
- All skills practiced in meaningful context
Our goal is to help you become the educator your child needs. We teach you the necessary approach to help your child reach their full potential. The good news is that these teaching methods benefit all students, helping everyone become competent and independent learners.
Do I Need a Special Dyslexia Reading Program or Writing Program?
Researchers have identified the underlying causes of dyslexia and the strategies students need for successful learning. Students with dyslexia have a less robust phonological processing system, so they struggle to learn and recall automatic sight words and basic spelling patterns. These students learn best using evidence-based teaching methods that employ consistent practice and application. All of this must be presented in a comprehensive curriculum that combines reading, writing, and spelling.
Our curriculum and online educator training courses provide exactly that. We show you how to work with kids to improve their foundational skills. We help you understand how reading works and how best to teach students with dyslexia, so you can feel confident that your student is on the right path to success.
Best of all, we know first hand that our strategies work! We have over four decades of experience working with students who struggle in the areas of listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Every student can succeed!
Our programs are appropriate for all age levels, but it is the student's skill level that should be the primary consideration for determining where to begin.
Are There Tests for Dyslexia and Should I Get My Student Tested?
Testing looks at three key sublexical skill areas that indicate dyslexia:
- Phonological Processing
- Phonological Memory
- Rapid Automatic Naming
Assessments also determine the student’s grade-level skills in the following lexical areas:
- Spelling
- Reading accuracy
- Reading fluency
- Reading comprehension
- Listening comprehension
Because some students with dyslexia may also have an underlying Developmental Language Disorder, an inventory of the student’s speech and language development should be obtained. If there is a history of delay, the assessment should also evaluate skills in the following areas:
- Language Working memory
- Syntax
- Sentence formulation
- Vocabulary
Contact your local chapter of the International Dyslexia Association: ask for a referral for an educational psychologist, neuropsychologist, or speech-language pathologist who tests for dyslexia. If you contact your local school system or Children's Hospital, be aware that they may not have professionals who specialize in dyslexia.
If you are still unsure about testing but would like answers to your specific questions, schedule a coaching session with a Rooted in Language expert. We can help you develop a learning plan and path forward for your student!










